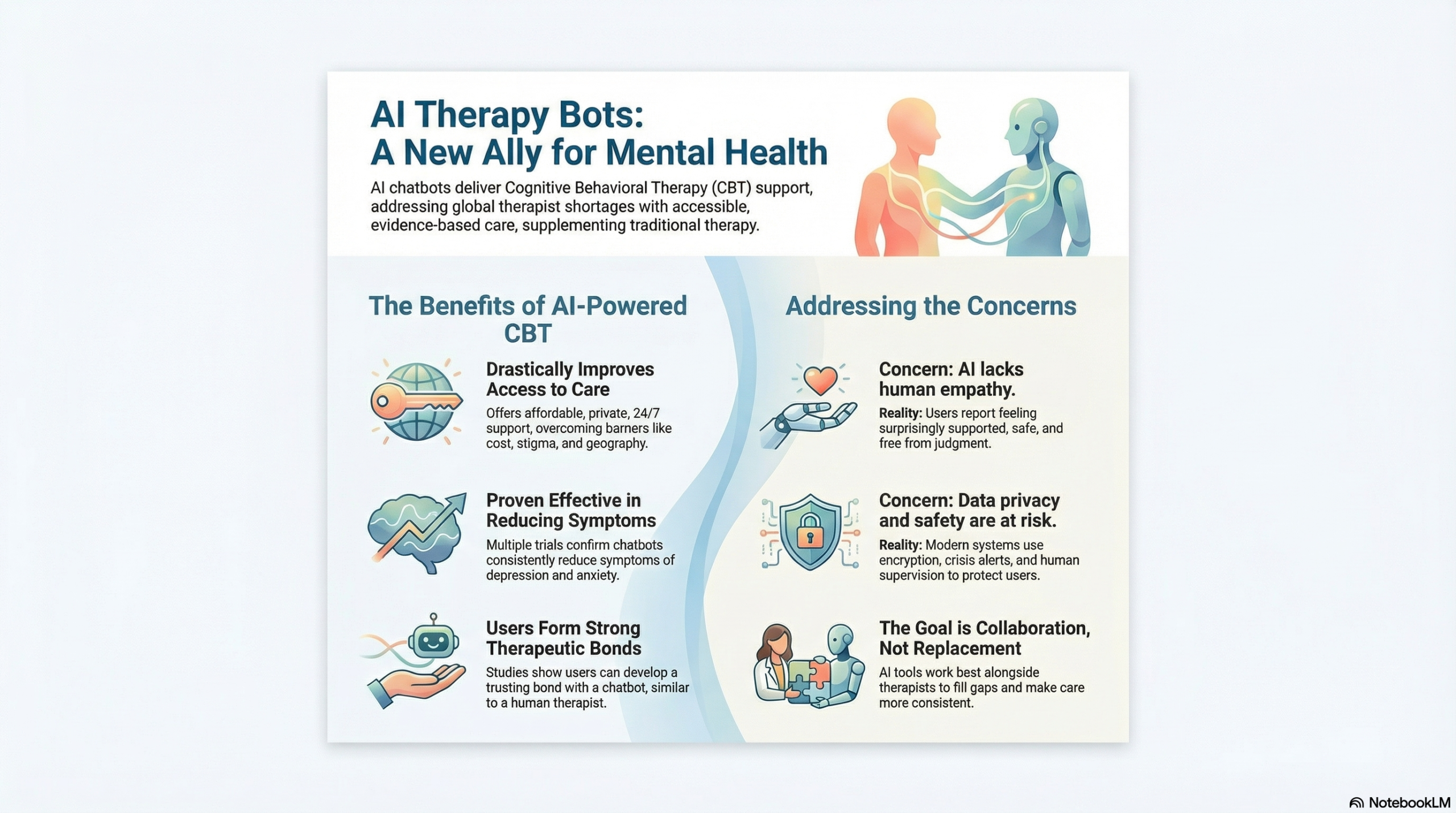
Can a machine really help heal the human mind? Around the world, mental health problems are increasing while the number of trained therapists remains far too low to meet the need. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is widely regarded as one of the most reliable and evidence-based treatments for anxiety and depression. Yet access to it is often restricted by high treatment costs, stigma, and shortages of qualified professionals.
In response, artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots like Wysa, Woebot, and Tess have emerged to deliver CBT-based support through simple text conversations. These chatbots guide users to challenge negative thoughts, build healthier coping habits, and reflect on their emotions, all from the privacy of their own devices. Although some doubt whether technology can truly replace human empathy, growing evidence shows that AI chatbots can play a valuable role alongside traditional therapy. They should be used to deliver Cognitive Behavioral Therapy as supportive tools because they make mental health care more accessible and have proven effective when guided by human oversight.
AI Chatbots making mental health care more accessible
One of the biggest strengths of AI-based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is how much it improves access to mental health care. In many parts of the world, therapy is concentrated in cities, leaving people in rural or underserved areas without support. AI chatbots help close this gap by offering affordable, private, and round-the-clock access through smartphones. They also remove the fear of being judged, which often stops people from seeking help in person.
In a review of patient perspectives, Abd-Alrazaq et al. (2021) found that many users appreciated chatbots for being easy to reach, confidential, and less intimidating than face-to-face therapy. Similarly, Habicht et al. (2024) reported that a self-referral chatbot led to a noticeable rise in people, especially those from minority groups, accessing mental health services for the first time. Together, these findings show that AI chatbots don’t just offer convenience; they open doors for people who might otherwise be left out of care. By bridging these gaps, they make psychological support more inclusive and available to everyone who needs it.
AI Chatbots as an effective solution
Beyond making therapy more accessible, there is growing proof that AI-based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) can truly help people feel better. Chatbots built on CBT principles use simple but effective techniques like mood tracking, guided journaling, and thought reframing to help users manage their emotions. In a mixed-methods study, Beatty et al. (2022) found that people using the Wysa chatbot developed a strong therapeutic bond with it, almost comparable to the connection they might form with a human therapist. Building that sense of trust and understanding is one of the most important predictors of successful therapy.
Likewise, Harrer et al. (2023) reviewed multiple trials and concluded that AI chatbots consistently reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety across different short-term interventions. Together, these studies show that when thoughtfully designed, AI chatbots can do more than just offer self-help tips. They can deliver the core elements of CBT and support real psychological improvement.
A Tool to Assist, Not Take Over
Some people believe AI can never replace the warmth and intuition of a real therapist. They argue that chatbots might miss emotional cues or respond in ways that feel mechanical rather than empathetic. Others worry about privacy, after all, sharing personal thoughts with an algorithm can feel risky. These are valid concerns, but research shows that many of these challenges are being addressed. In a 2024 study, Siddals et al. found that users described their experiences with AI chatbots as surprisingly supportive and emotionally validating. Many even said the conversations felt safe and judgment-free, which encouraged them to open up.
Similarly, Meadi et al. (2025) reviewed ethical issues in mental health chatbots and noted that most modern systems now use encryption, crisis-response alerts, and human supervision to protect users and ensure safety. When used alongside therapists rather than instead of them, chatbots can fill the gaps between sessions, provide early screening, and make care more consistent. Instead of undermining therapy, AI when guided by ethical safeguards, can make the whole system stronger and more responsive.
Conclusion
AI chatbots aren’t here to replace human therapists, they’re here to make care reach further. They offer a practical, affordable, and research-backed way to support people who might otherwise go without help. Recent studies show that CBT-based chatbots can ease symptoms of anxiety and depression while helping users feel understood and supported. Of course, these tools still have limits, but with proper human oversight, clear ethical guidelines, and strong data protection, their risks can be managed.
The true aim is not to choose between humans and AI, but to bring their strengths together. If used responsibly, chatbots can make mental health care more accessible, continuous, and stigma-free. The question is no longer whether we should use them, but how soon can we make sure that anyone who needs support has one within reach.